
Virus scanning: this only launches the Comodo Rescue Disk for now.

#Kon boot .torrent windows 8.1#
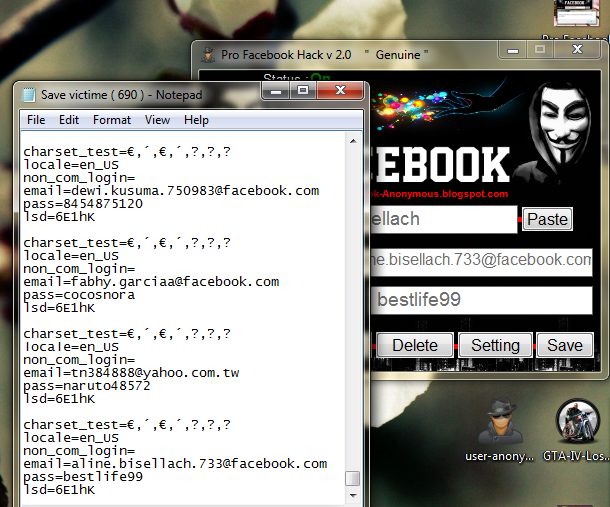
These include: EaseUS Partition Master, HDDExpert, NTFS Permissions Tool, backup tool, Dead Pixel checker, CPU-Z, RegAlyzer, Dr.Web CureIt, Kaspersky TDSSKiller, Malwarebytes Anti-Malware and Autoruns.

#Kon boot .torrent Pc#
You can access all sorts of programs right there, and even more if you’re using the version of the toolkit that comes with PortableApps (this one). This includes many tools to help you troubleshoot your PC MediCat USB is a bootable troubleshooting environment that comes with a Windows PE boot environment and troubleshooting tools. The author of MediCat DVD designed the bootable toolkit as an unofficial successor to the popular Hiren’s Boot CD boot environment . Results show that the framework is very trustable for the resource sharing with fairness and reliability in distributed/P2P systems.MediCat Boot USB v21.06 – Versatile and complete rescue USB Boot kit for KTV Experimental simulation used for evaluating and validating the performance of the proposed framework. Reliability is implemented by using the trust model where reliability levels are modeled for realization of reliability in the system. Every system can use the resources of other systems on payments from its salary and can select the resource in competitive environment. For fairness we use the concept of accounting systems where the entities of the systems are bank accounts, salaries and resource rates. In this paper, we propose a framework for fair and reliable resource sharing in distributed/P2P systems. Moreover a resource provider may not be providing efficient and reliable services to other peers/nodes and is just sharing resources for the sake of resource sharing. For example, a peer/node may be willing to be a resource consumer and not a provider. They thus suffer from freeloaders, that are, participants who consume many more resources than they contribute.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) and distributed systems are typically designed around the assumption that all peers/nodes will willingly contribute resources to each other. This paper will discuss the tests that were performed, how they were evaluated, as well as some improvements that could be made to future tests to enhance server-side efficiency. Current results show the BitTorrent scenario allows clients to share the burden of data distribution on BOINC with almost no negative influence on compute time. The BOINC server, on the contrary, showed an unexpectedly low bandwidth output when seeding the file, as well as spikes on CPU usage. Our preliminary results indicate that the BitTorrent client had a negligible influence on the BOINC client’s computation time, even in the case where it was seeding extensively. Additionally, we measured the impact of the BitTorrent components in both the BOINC client and server, and compared it with the original implementation. To achieve this, we developed a prototype that adds BitTorrent functionality for task distribution and conducted small-scale tests of the environment. Our goal was to decentralize BOINC’s data model to take advantage of client network capabilities. In this paper we show how we applied BitTorrent data distribution techniques to the BOINC middleware.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
